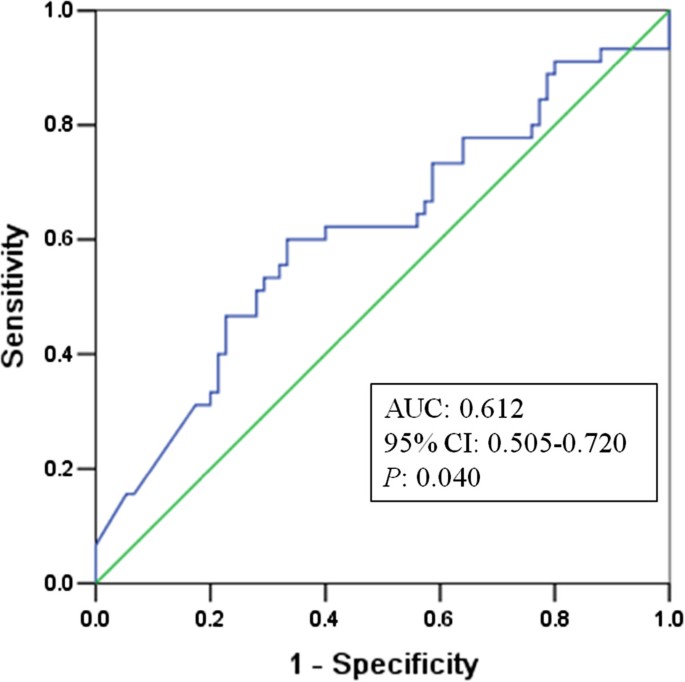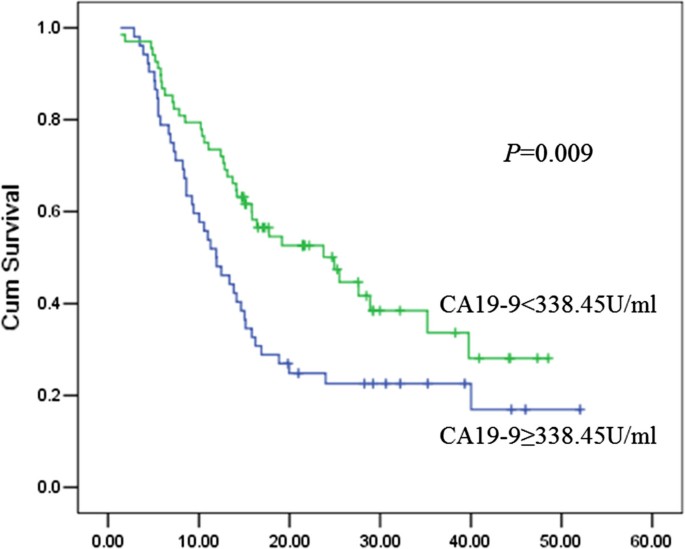
Elevated serum CA19-9 level is a promising predictor for poor prognosis in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: a pilot study | World Journal of Surgical Oncology | Full Text
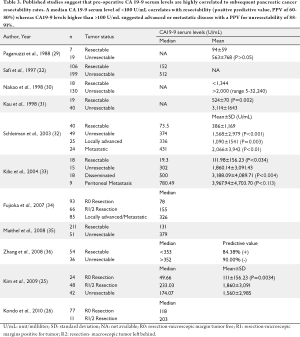
The clinical utility of serum CA 19-9 in the diagnosis, prognosis and management of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: An evidence based appraisal - Ballehaninna - Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology
Clinical Significance and Revisiting the Meaning of CA 19-9 Blood Level Before and After the Treatment of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Analysis of 1,446 Patients from the Pancreatic Cancer Cohort in a Single
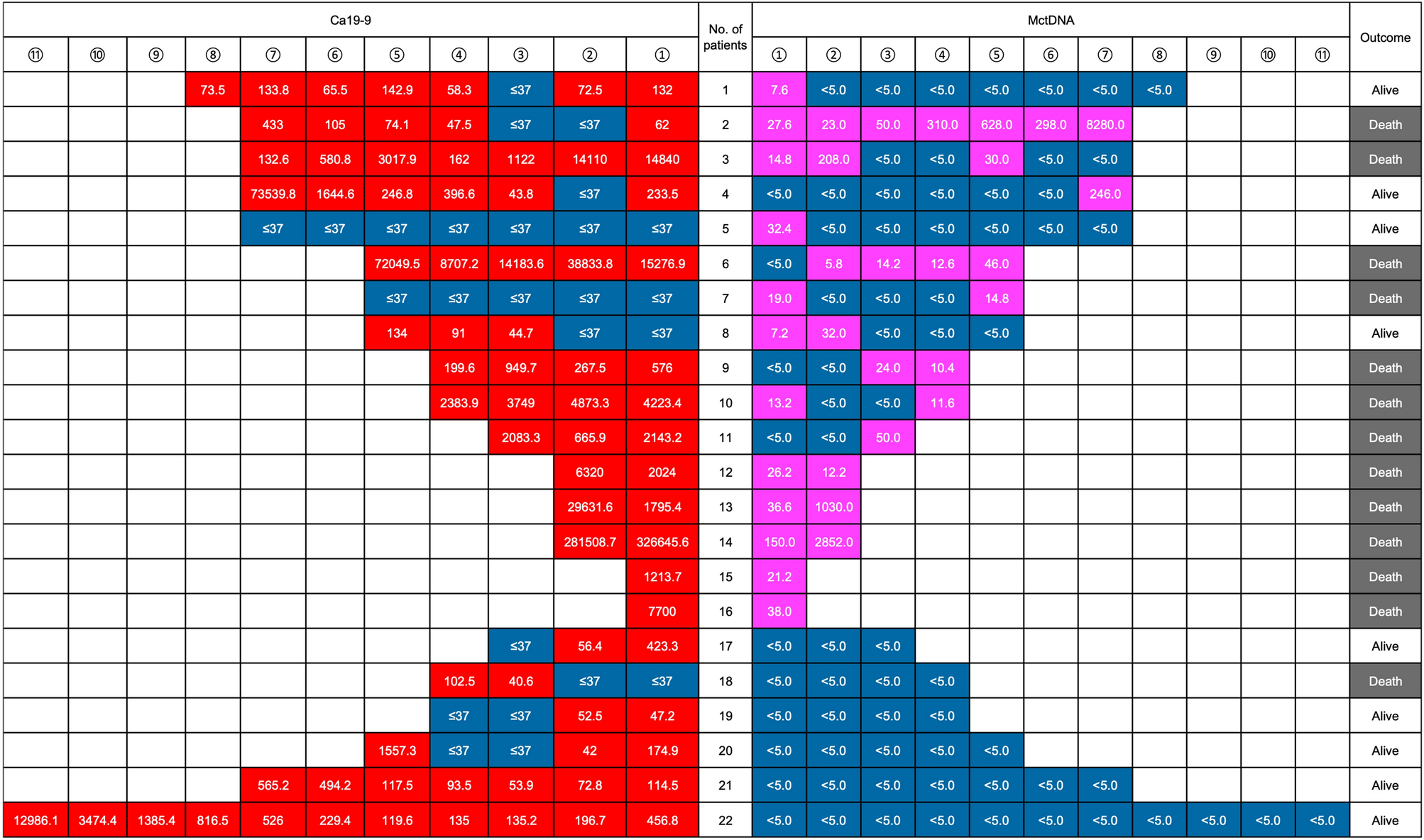
Optimal value of CA19-9 determined by KRAS-mutated circulating tumor DNA contributes to the prediction of prognosis in pancreatic cancer patients | Scientific Reports

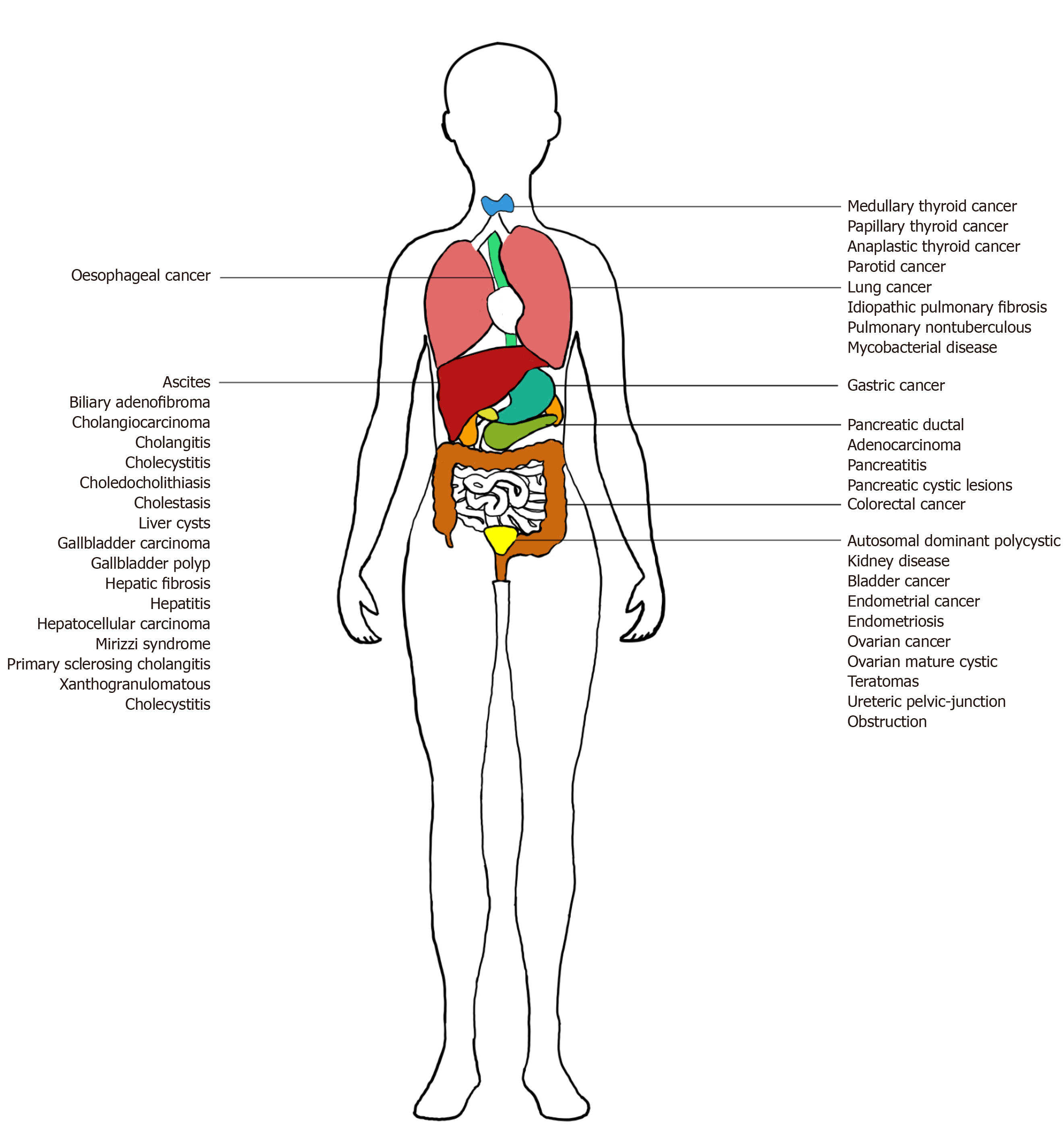
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 elevation without evidence of malignant or pancreatobiliary diseases | Scientific Reports

The significance of elevated tumor markers among patients with interstitial lung diseases | Scientific Reports
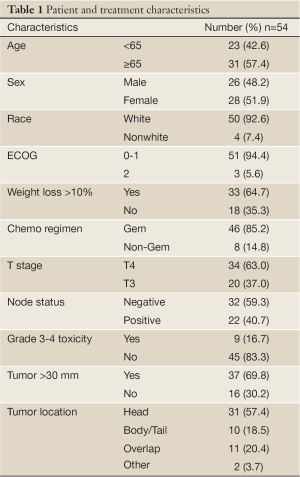
Change in CA 19-9 levels after chemoradiotherapy predicts survival in patients with locally advanced unresectable pancreatic cancer - Yang - Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology
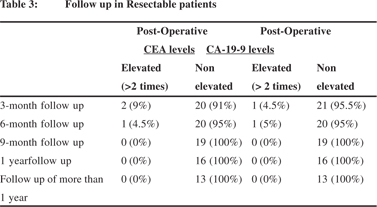
Evaluating the efficacy of tumor markers CA 19-9 and CEA to predict operability and survival in pancreatic malignancies
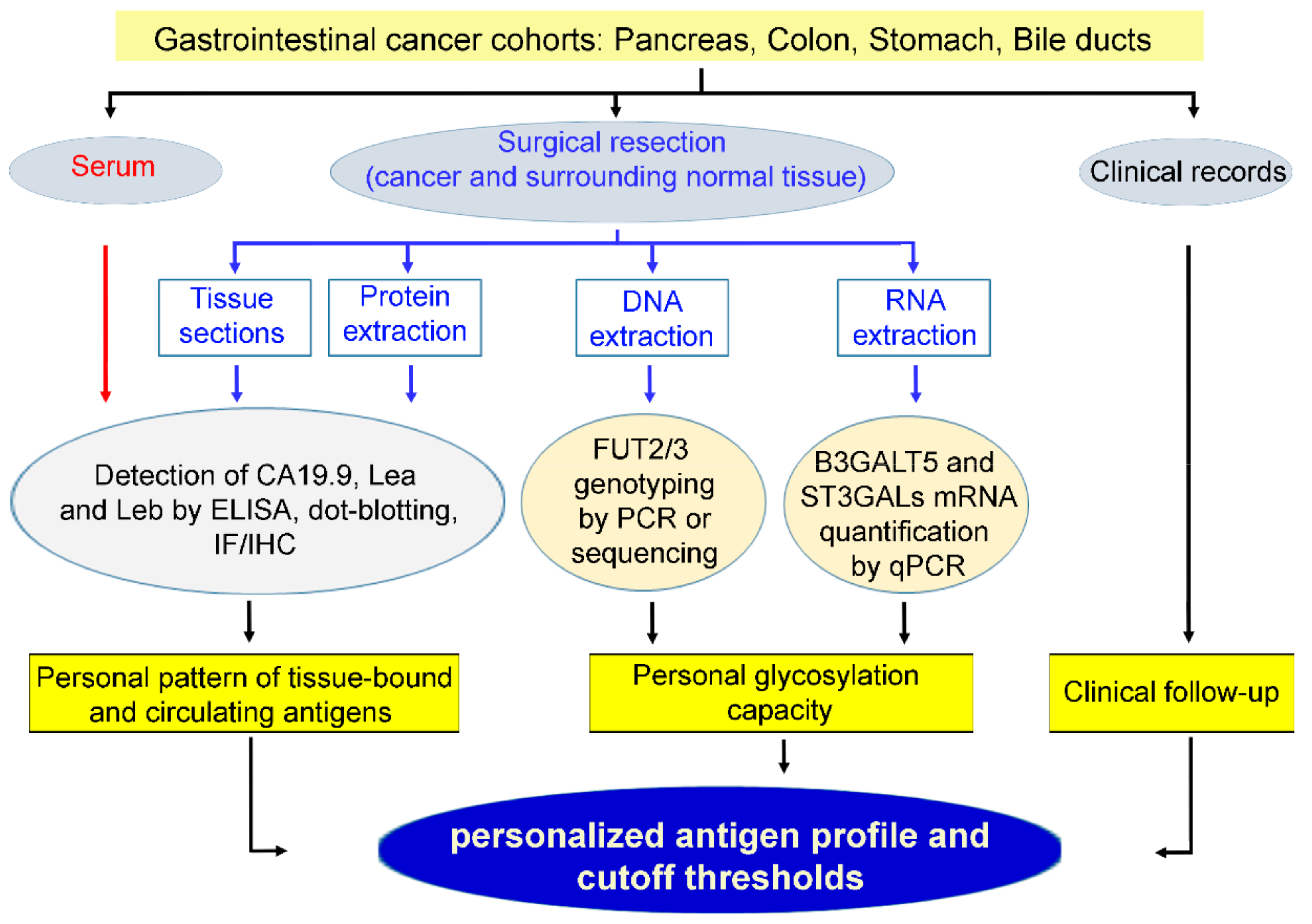
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Complementary Use of Carbohydrate Antigens Lewis a, Lewis b, and Sialyl-Lewis a (CA19.9 Epitope) in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Biological Rationale towards a Personalized Clinical Application

CA 19-9 tumour-marker response to chemotherapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer enrolled in a randomised controlled trial - The Lancet Oncology
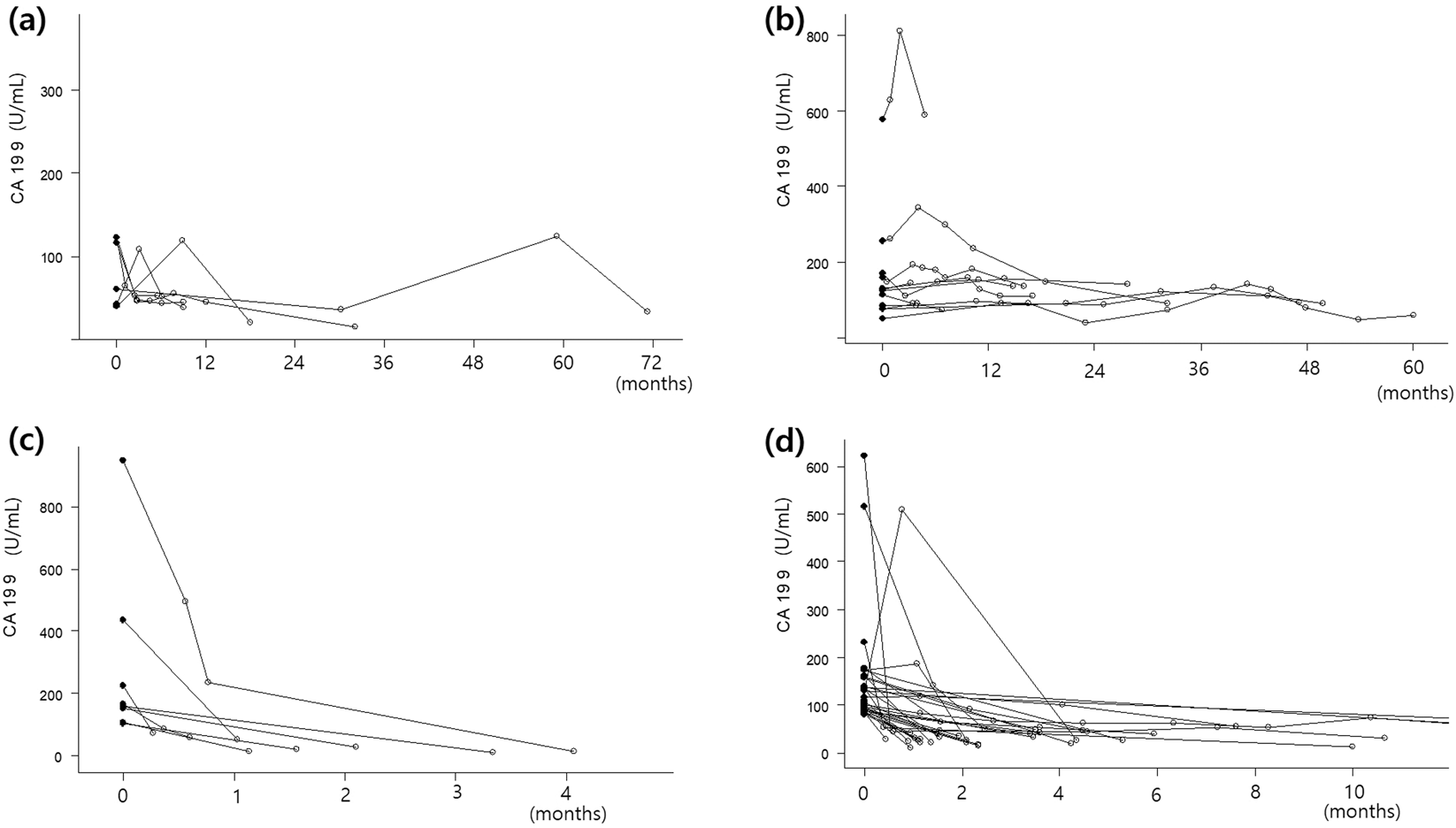
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 elevation without evidence of malignant or pancreatobiliary diseases | Scientific Reports
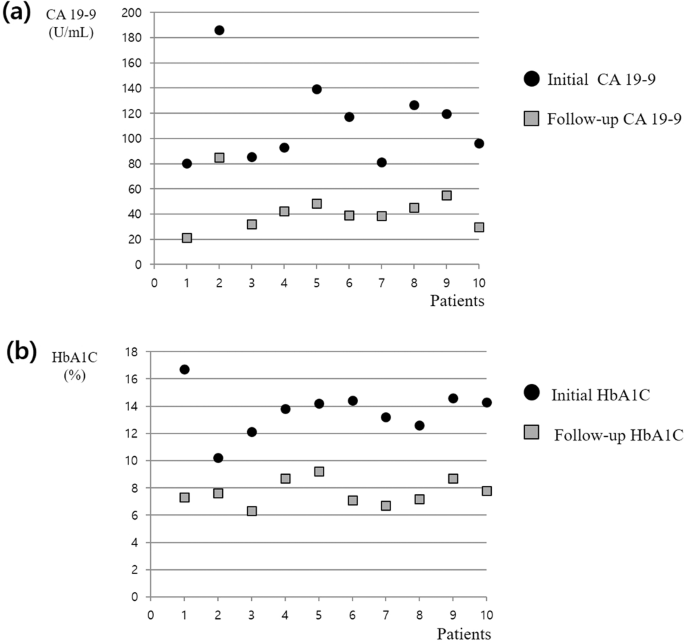
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 elevation without evidence of malignant or pancreatobiliary diseases | Scientific Reports

Gene Variants That Affect Levels of Circulating Tumor Markers Increase Identification of Patients With Pancreatic Cancer - ScienceDirect
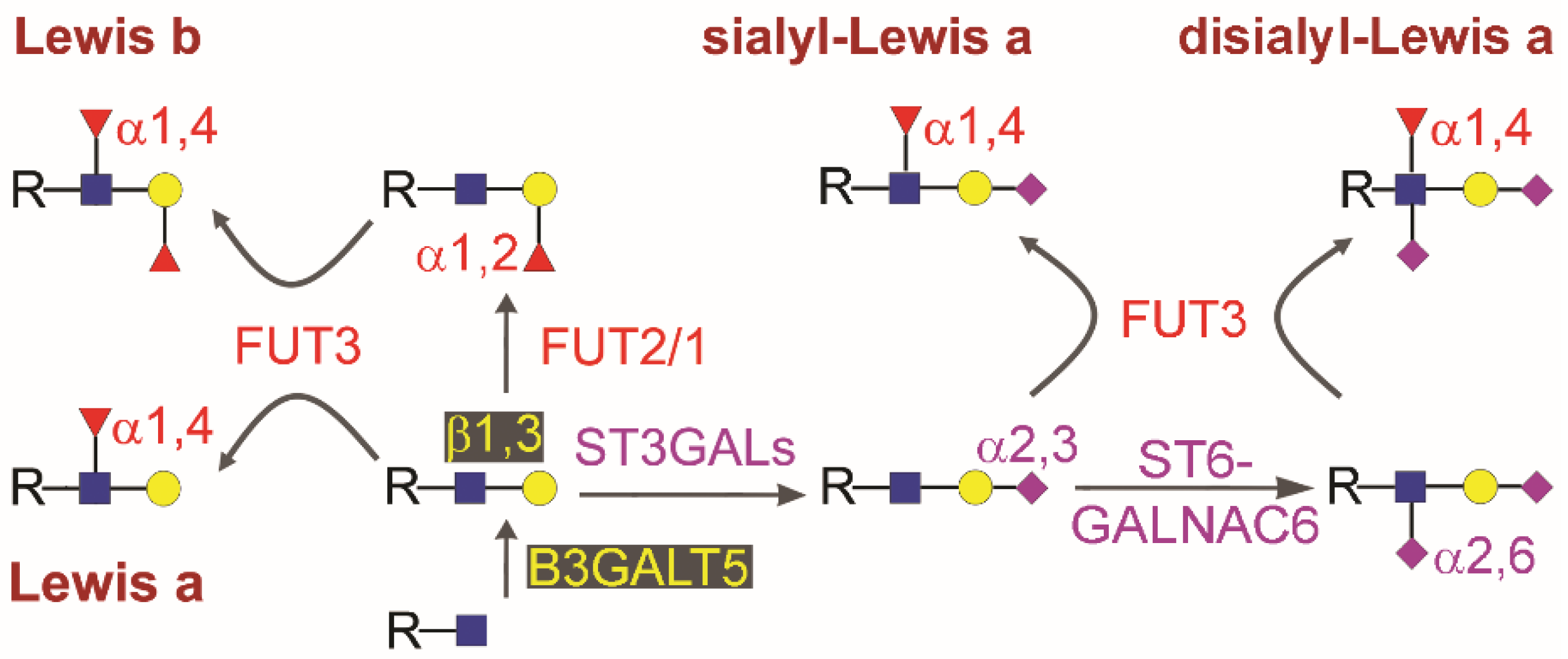
Cancers | Free Full-Text | Complementary Use of Carbohydrate Antigens Lewis a, Lewis b, and Sialyl-Lewis a (CA19.9 Epitope) in Gastrointestinal Cancers: Biological Rationale towards a Personalized Clinical Application